Learn About Your Horse's Teeth
Updated on 04/26/24
Unlock the Secrets of Your Horse's Teeth: A Comprehensive Guide for Equestrians
As horse owners and enthusiasts, we have a profound responsibility to ensure the well-being of our equine companions. Understanding the intricacies of their dental health is an essential aspect of this care. Horse's teeth play a crucial role in their overall health, influencing their ability to eat, groom, and perform various activities. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the fascinating world of equine dentistry, empowering you with the knowledge to provide optimal dental care for your beloved horse.
Dental Anatomy: A Foundation for Understanding
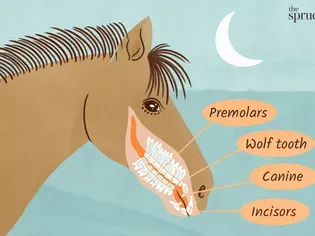
Equine teeth are a marvel of nature, exhibiting a unique structure and development process. Understanding their anatomy is pivotal for identifying potential dental issues and promoting oral health.
* Incisors: The front teeth, used for grazing and cropping grass.
* Canines: Present only in male horses, used for fighting and dominance rituals.
* Premolars and Molars: The "cheek teeth," responsible for grinding and chewing food.
* Wolf Teeth: Small, vestigial teeth located in front of the premolars, often extracted to prevent discomfort.
* Tushes: Enlarged canine teeth occasionally found in female horses, used for defense.
Common Dental Problems: Recognition and Treatment
Dental issues are common in horses, ranging from minor irregularities to severe abnormalities. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent pain, discomfort, and long-term health consequences.
* Malocclusion: Misalignment of the upper and lower teeth, causing difficulty eating and facial asymmetry.
* Dental Caries: Bacterial infections that damage teeth, leading to pain and tooth loss.
* Periodontal Disease: Infection and inflammation of the gums, supporting structures, and root surfaces, potentially causing tooth loss and systemic health issues.
* Abscess Formation: Bacterial accumulation beneath the tooth surface, resulting in swelling, pain, and potential systemic infection.
* Fractures and Trauma: Damage to teeth caused by falls, accidents, or chewing on hard objects.
Routine Dental Care: Essential for Optimal Health
Regular dental care is a cornerstone of equine preventive healthcare. By implementing these practices, you can proactively prevent problems and maintain your horse's oral health.
* Dental Exams: Annual or semi-annual examinations by a qualified veterinarian to assess tooth condition, identify potential issues, and perform necessary treatments.
* Floating: A procedure that smooths sharp tooth edges, preventing cuts and sores in the mouth.
* Extractions: Removal of damaged or problematic teeth to alleviate pain and prevent infection.
Special Considerations for Senior Horses
As horses age, their dental needs evolve. Understanding these changes and providing appropriate care is essential for their well-being.
* Dental Wear: Teeth naturally wear down with age, potentially leading to malocclusion and other issues.
* Periodontal Disease: Age-related immune system changes can increase susceptibility to periodontal disease.
* Geriatric Floating: Regular floating is recommended to manage dental wear and maintain oral health in senior horses.
Importance of a Healthy Diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in equine dental health. Certain foods and feeding practices can contribute to dental problems or accelerate their progression.
* Hay and Grass: Fiber-rich roughage promotes chewing and natural tooth wear.
* Grains and Concentrates: Excessively sugary or sticky feeds can stick to teeth, increasing the risk of caries.
* Hard Treats and Chews: Avoid feeding horses hard objects that can damage teeth or break them.
Additional Tips for Horse Owners
Empowering yourself with these additional tips will further enhance your horse's dental well-being:
* Observe Your Horse's Behavior: Changes in eating habits, facial asymmetry, or chewing discomfort can indicate dental problems.
* Monitor Dental Hygiene: Occasionally check your horse's mouth for any signs of infection or inflammation.
* Consider Dental Insurance: Veterinary insurance can help offset the costs associated with unexpected dental expenses.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of your horse's teeth is essential for providing optimal dental care and ensuring their overall health and well-being. By recognizing common dental problems, implementing routine dental care practices, and considering special considerations for senior horses and their diet, you can become an advocate for your equine companion's oral health. Remember, a healthy mouth leads to a happier and more comfortable horse.
Explore More Pets

Pony Breeds
The Difference Between Horses and Ponies

Horse Diseases & Conditions
What Do I Do If My Horse Colics?

Pony Breeds
Horse and Pony Care by the Day, Week, Month and Year

Horse Grooming
Mange in Horses

Horse Diseases & Conditions
Grease Heel in Horses

Light Horse Breeds
Gypsy Vanner Horse Breed Profile

Horse Diseases & Conditions
Girth Galls and Saddle Sores

Pony Breeds
Shetland Pony Breed Profile