Rapid Breathing In Cats
Updated on 04/26/24
Title: Rapid Breathing in Cats: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction
Rapid breathing in cats, known as tachypnea, is a common clinical sign that can indicate a wide range of underlying health issues. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for tachypnea is crucial for cat owners to ensure their feline companions' well-being. This comprehensive guide will delve into the complexities of rapid breathing in cats, providing valuable insights and practical advice.
Understanding Tachypnea
Normal respiratory rates for cats range from 15 to 30 breaths per minute. Tachypnea is defined as a respiratory rate exceeding 30 breaths per minute. It can be a sign of various respiratory, cardiovascular, or metabolic conditions.
Causes of Tachypnea in Cats
* Respiratory Conditions:
* Asthma
* Pneumonia
* Pleural effusion (fluid in the chest cavity)
* Respiratory tract infections
* Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP)
* Cardiovascular Conditions:
* Heart failure
* Arrhythmias
* Pericardial effusion (fluid around the heart)
* Metabolic Conditions:
* Anemia
* Hyperthyroidism
* Fever
* Other Causes:
* Obesity
* Stress
* Pain
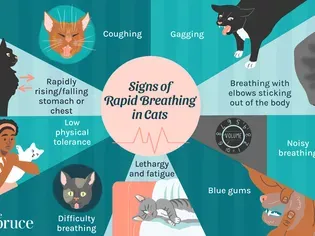
Symptoms of Tachypnea in Cats
* Rapid breathing (over 30 breaths per minute)
* Open-mouthed breathing
* Labored breathing
* Wheezing
* Coughing
* Lethargy
* Loss of appetite
Diagnosis of Tachypnea in Cats
Diagnosing the underlying cause of tachypnea in cats requires a thorough physical examination, a detailed history, and diagnostic tests. These may include:
* Auscultation of the chest to listen for abnormal lung sounds
* Blood tests to check for anemia, infection, or metabolic abnormalities
* Radiography (X-rays) to visualize the lungs and heart
* Echocardiography to assess heart function
* Ultrasound to detect pleural effusion
Treatment for Tachypnea in Cats
Treatment for tachypnea in cats depends on the underlying cause. The goal is to address the primary issue and alleviate the symptoms of rapid breathing.
* Respiratory Conditions: Bronchodilators, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications
* Cardiovascular Conditions: Diuretics, heart medications, anti-arrhythmic medications
* Metabolic Conditions: Management of underlying disease, such as treatment for anemia or hyperthyroidism
* Other Causes: Weight management, stress reduction, pain medication
Prevention of Tachypnea in Cats
While not all causes of tachypnea can be prevented, there are certain measures cat owners can take to minimize the risk:
* Regular veterinary checkups for early detection and treatment of respiratory or cardiovascular issues
* Vaccinations against respiratory infections
* Maintaining a healthy weight
* Managing stress through enrichment and a positive environment
* Providing a clean and smoke-free living environment
Conclusion
Rapid breathing in cats can be a sign of various health problems, ranging from minor respiratory infections to life-threatening conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for tachypnea is essential for cat owners to ensure prompt and appropriate care. By seeking veterinary attention when rapid breathing is noted, cat owners can contribute to the early detection and effective management of underlying health issues, promoting the health and well-being of their feline companions.
Explore More Pets

Cat Behavior Problems
How to Stop Aggression in Kittens

Long-Haired Cat Breeds
Siberian Cat: Breed Profile, Characteristics, & Care

Cat Behavior Problems
How to Stop Kittens From Scratching and Biting

Long-Haired Cat Breeds
Turkish Angora: Cat Breed Profile, Characteristics & Care

Basic Training
How to Socialize Your Kitten

Short-Haired Cat Breeds
Cute Pictures & Facts About Calico Cats & Kittens

Litter Box Training
Training Your Kitten to Use the Litter Box

Long-Haired Cat Breeds
10 Fun Facts About White Cats